A new research study entitled – Covid-19 contagion via aerosol particles – comparative evaluation of indoor environments with respect to situational R-value – by scientists at the Berlin Institute of Technology (TU Berlin) / Hermann-Rietschel-Institut in Germany has concluded that museums are safer than almost any other indoor environment. This, it says, assumes that safety guidelines are being followed.
Significantly, the study finds that that the risk of COVID-19 transmission is far lower in museums and theatres than in supermarkets, restaurants, offices, or public transport.
Led by Martin Kriegel and Anne Hartmann, the research conducted a comparative evaluation of indoor environments to assess the risk of infection via aerosol particles. The analysis considers the average length of stay in a given space (two hours at a museum; eight hours in an office; one hour in a supermarket; etc.), the quality of the airflow, the type of activity carried out in the space, and the dose of aerosol particles inhaled by people in a room, among other variables. Each environment has been given an R-value, indicating the number of people that one COVID-19 carrier can infect on average.
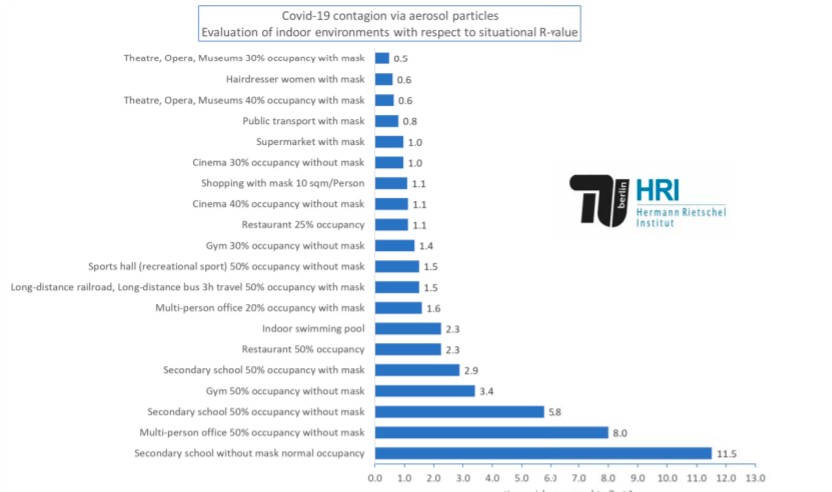
Image courtesy TU / Hermann-Rietschel-Institut
The study, which was reported in Hyperallegenic.com, says that researchers found that if kept at 30% capacity with everyone wearing a mask and following proper precautions, museums, theatres, and operas are safer than any other activity studied. In museums, the R-value stands at 0.5 compared to 0.6 in hair salons and 0.8 in public transportation.
Explanation example:
A person with mask in a supermarket has a risk with the value 1. This means, that in this situation a maximum of one other person will be infected. In comparison a multi-person office with a 50% reduced occupancy, but without wearing a mask at the workplace, has a value of 8. This means, that the risk in this situation is 8-times higher than in the supermarket. In contrast, a visit to a theatre in a meeting place with 30% reduced occupancy and with wearing a mask while sitting is just half as risky as in the supermarket.
To read the study and delve into the figures, click here.
Content Team
Work in Mind is a content platform designed to give a voice to thinkers, businesses, journalists and regulatory bodies in the field of healthy buildings.




